August 2022
Creating sustainable use of space, with strong support from the world´s leading nations
Deorbit-systems to speed up sailing satellites down from orbits to become a decisive cornerstone in creating sustainable use of space, with strong support from the world´s leading nations.
ADEO, the world´s leading autonomous deorbit system, will also guide yours sat on angel wings to nirvana when its time has come to give room to newcomers!
Please also read political standpoints here:
https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/07-2022-NATIONAL-ORBITAL-DEBRIS-IMPLEMENTATION-PLAN.pdf
and here
REGULATION (EU) 2021/696 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL
of 28 April 2021
establishing the Union Space Programme and the European Union Agency for the Space Programme and repealing Regulations (EU) No 912/2010, (EU) No 1285/2013 and (EU) No 377/2014 and Decision No 541/2014/EU
and here
SECURE WORLD FOUNDATION
Statement under Agenda Item – 8. Space Debris
February 2022
Fifty-ninth Session of the Scientific and Technical Subcommittee of the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space

August 2022
ADEO deorbit sail product family continues to grow: Successful financing round for industrialization of ADEO Medium for constellation satellites
Paris-Munich. August 1, 2022.
Just one last signature, and the success story of the almost decade-long development of the European deorbit sail ADEO by HPS is going to find its seamless continuation: the model ADEO M for medium satellites of 100-700 kilo weight on orbits up to 900 km altitude – so, typical representatives of the currently almost exponentially growing constellation projects – will be made fit for series production and distribution on the commercial market by the HPS Group in Germany and Romania.
Parallely, additional features of ADEO N (Nano) will be developed. ADEO M follows the versions ADEO N and ADEO L (Large), which have already been on the market for 1.5 years. With the third model, HPS now closes the last gap in its product portfolio and addresses in particular the booming NewSpace market thanks to maturity level TRL 9 and growing flight heritage on missions of various carriers with world-leading deorbit automatic.
This leadership is also a result of the steady and now renewed support from Europe’s GSTP technology program and its German SME initiative on the part of ESA and DLR Space Agency. „Everyone is talking about space debris; thanks also to ESA´s “Zero Debris Initiative”, with ADEO, our customers are making sure it doesn’t even happen.
This is the only way a clean-green mission works, the only way the EU’s Green Deal becomes a reality also in space.“
For each satellite on LEO there is a suitable ADEO, which accelerates deorbiting by a factor of about 20. All interested companies get the exact forecast free of charge and super fast; all they have to do is feed our globally unique „ADEO deorbit timer“ with the data of their satellite and then let the algorithms do their jobs,“ says HPS CEO Dr. Ernst K. Pfeiffer. As in the case of ADEO N and ADEO L, already now orders for new satellite projects are also being accepted for ADEO M, shortly before the start of series production, in order to harmonize planning and production processes on both the HPS and the customer sides.

Juli 2022
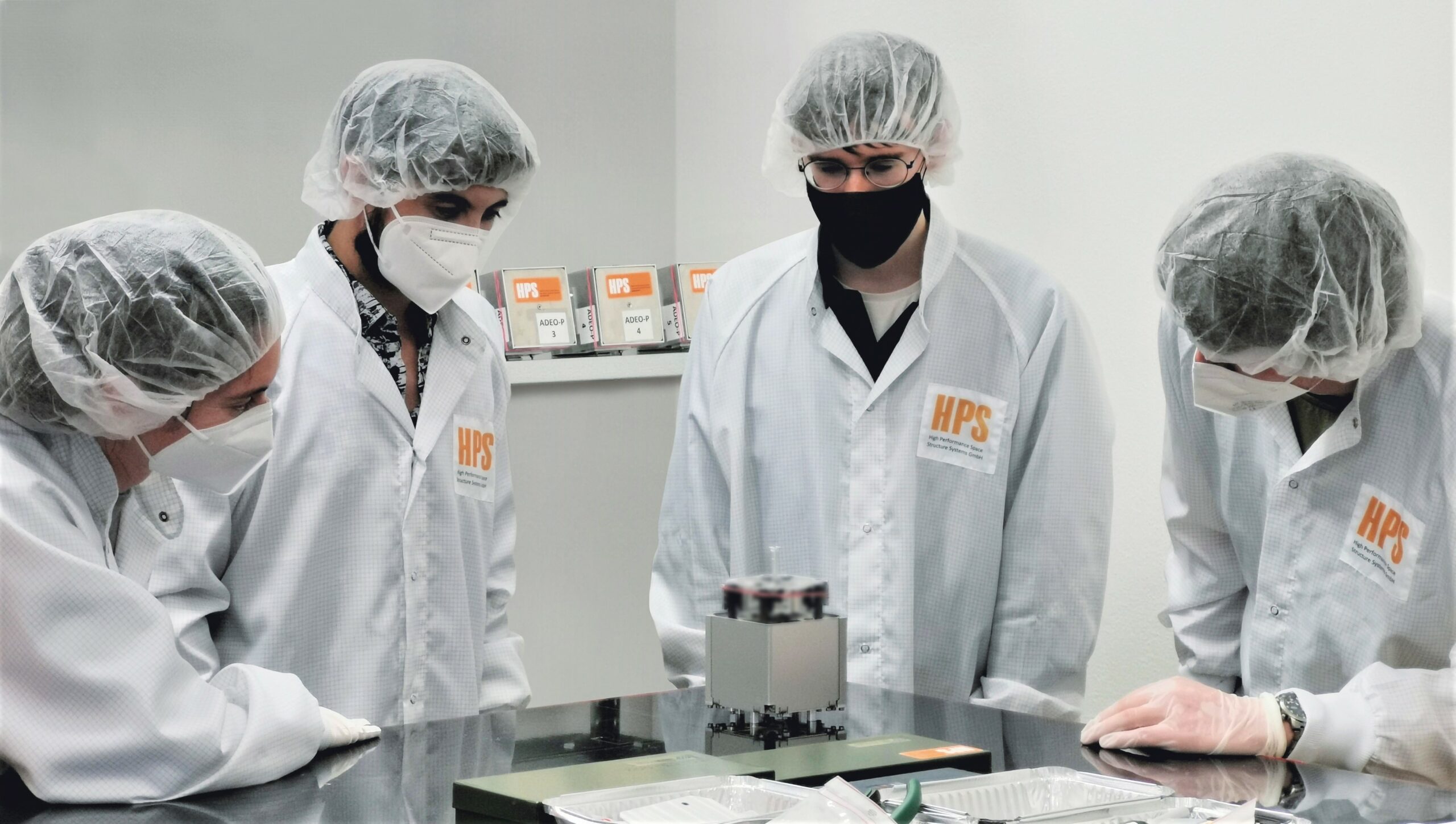
Flug von ADEO-N3 am Ende des Jahres 2022
In der Hoch-Zeit der Sommerferien herrscht bei HPS in München Hochdruck in den Vorbereitungen für die dritte Mission des innovativen Weltraumbremssegels ADEO, welches sich automatisch am Ende der Mission entfaltet und „seinen“ Satelliten bis zu 20-mal schneller zum Verglühen in die Atmosphäre treibt. So wird Schrott vermieden und Raumfahrt nachhaltig.
Schon Ende August wird es in Italien zur Montage auf dem ION „Satellite Carrier“, D-Orbit´s „orbital transfer vehicle (OTV)“ angeliefert. Es ist die ADEO-N-Version für Kleinsatelliten mit einer Segelfläche von 5 qm.
Gegen Ende 2022 wird eine Falcon 9 Rakete von SpaceX den Satelliten in einen Orbit mit Mittlerer-Inklination bringen. Mit der bis Ende des Jahres dann angesammelten Flight Heritage wird ADEO 2023 in ein neues Raumfahrt-Zeitalter starten.
Denn zumindest für europäische Missionen bzw. Missionen von Europa aus wird es dann in aller Wahrscheinlichkeit keine Starts mehr ohne Deorbit-Tech an Bord mehr geben:
Der Green Deal der EU gilt dann auch für clean-green missions im Raum.

June 2022
Breaking News: ADEO dragsail by HPS as standard deorbit device for „Reflex Aerospace satellites“
Next milestone in commercializing ADEO dragsail for deorbit:
Reflex Aerospace (supplier of tailor made, high performance small satellite platforms) announces to use the automatic ADEO dragsail by HPS as standard deorbit device for their satellites. ADEO will guarantee a maximum deorbiting time of less than 5 years and contribute to Reflex Aerospace´s philosophy of responsible, sustainable and future-oriented space missions. Together we realize CleanGreen Space missions!

Dezember 2021
Weltpremiere: Deorbit-Turbosail „ADEO“ von HPS ausgewählt, um die Nachhaltigkeit der europäischen Konstellation zu sichern
Bis 2025 wird Europa über eine eigene Satellitenkonstellation verfügen, um souveräne Kapazitäten sowohl für kommerzielle als auch für institutionelle Kommunikationskanäle zu gewährleisten. Schnelles Internet, autonome Mobilität auf See, am Boden und in der Luft, automatischer Informationsaustausch zwischen technischen Einrichtungen, Unterstützung militärischer und humanitärer Aktionen und weitere Anwendungen für Behörden, Unternehmen und Bürger realisiert von einem Konsortium aus Reflex, Laser Spezialist Mynaric und Startdienstleister Isar Aerospace.
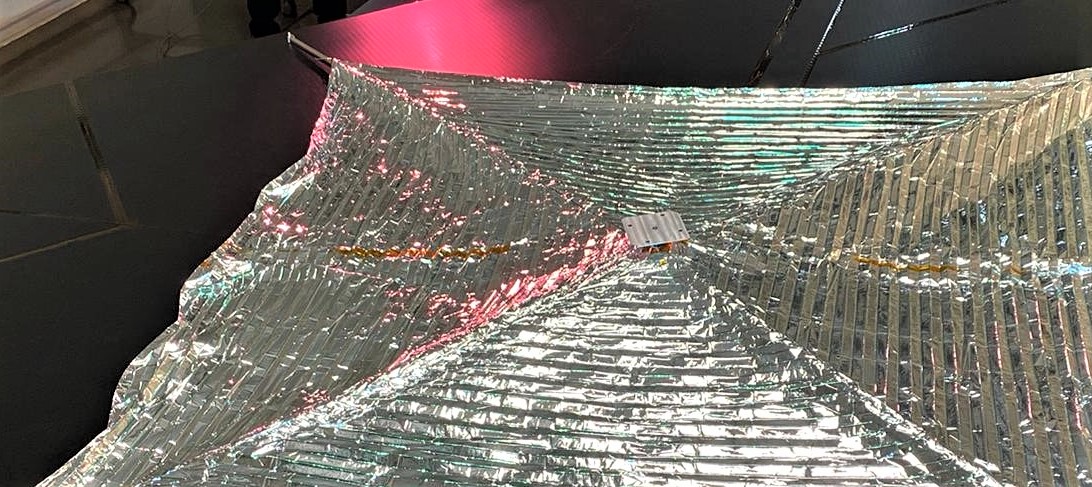
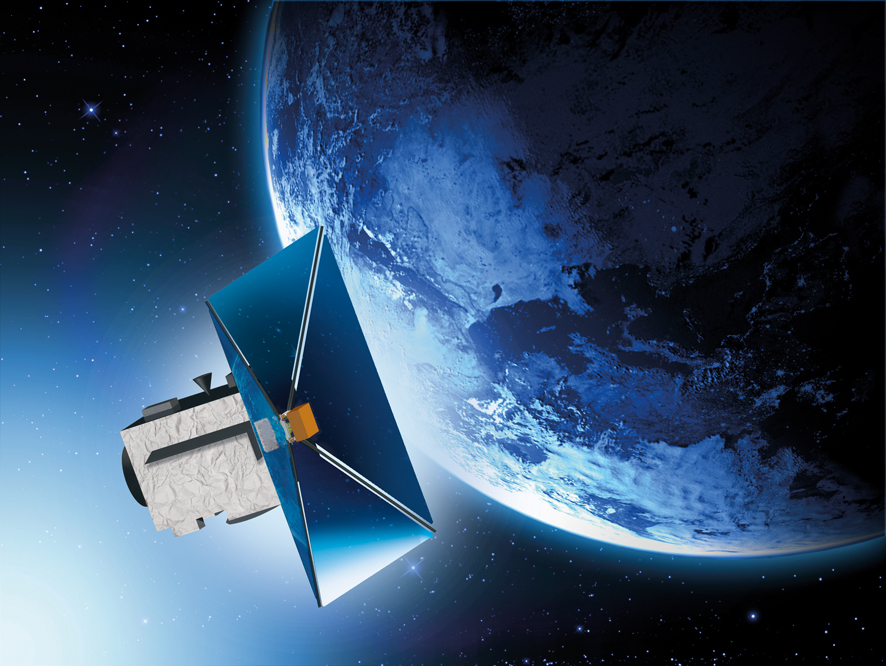
Auch die Europäische Kommission ist an einer solchen Konzentration von Innovationskräften sehr interessiert und hat das UN:IO-Konsortium für eine seiner beiden Studienausschreibungen ausgewählt, die sich an Unternehmen aus dem sogenannten „New Space“-Bereich richten und mit 1,4 Millionen Euro dotiert sind. Für die EU hat ein sicheres, sehr schnelles und vor allem souveränes Kommunikationsnetz für Europa oberste Priorität. Darüber hinaus muss es Nachhaltigkeitskriterien für den „Green Deal“ der EU erfüllen – und hier kommt ADEO ins Spiel: Das ADEO-Subsystem ist ein skalierbares, entfaltbare Komponente, welches die im Low Earth Orbit (LEO) vorhandene Restatmosphäre der Erde nutzt, um Satelliten zwischen 1 und 1.500 kg nach ihrem Ende der Lebensdauer passiv verschwinden zu lassen. Für das De-Orbit-Manöver wird eine große Oberfläche eingesetzt, die den Widerstandseffekt der Satellitenoberfläche deutlich vervielfacht. Dadurch wird die Widerstandskraft erhöht, was zu einem beschleunigten Abfall der Orbithöhe führt. Vorteilhaft an ADEO ist, dass es keine aktive Lenkung erfordert und zur passiven Lagestabilisierung ausgelegt werden kann, wodurch sie auch für nicht betriebsfähige, taumelnde Raumfahrzeuge anwendbar ist. Das passive ADEO-Subsystem benötigt weder zusätzlichen Antrieb noch Motor, was es im Vergleich zu aktiven Subsystemen leichter macht.
Nach jahrelanger Entwicklung, Tests und Schwerelosigkeits- und In-Orbit-Verifikationen feiert ADEO nun seine Weltpremiere als zentrales Element, das auf Engelsflügeln Nachhaltigkeit ins All bringt.

Juli 2021
Falcon 9 Rakete setzt erfolgreich innovative Technologie ein, um den Weltraum nachhaltig sauber zu halten
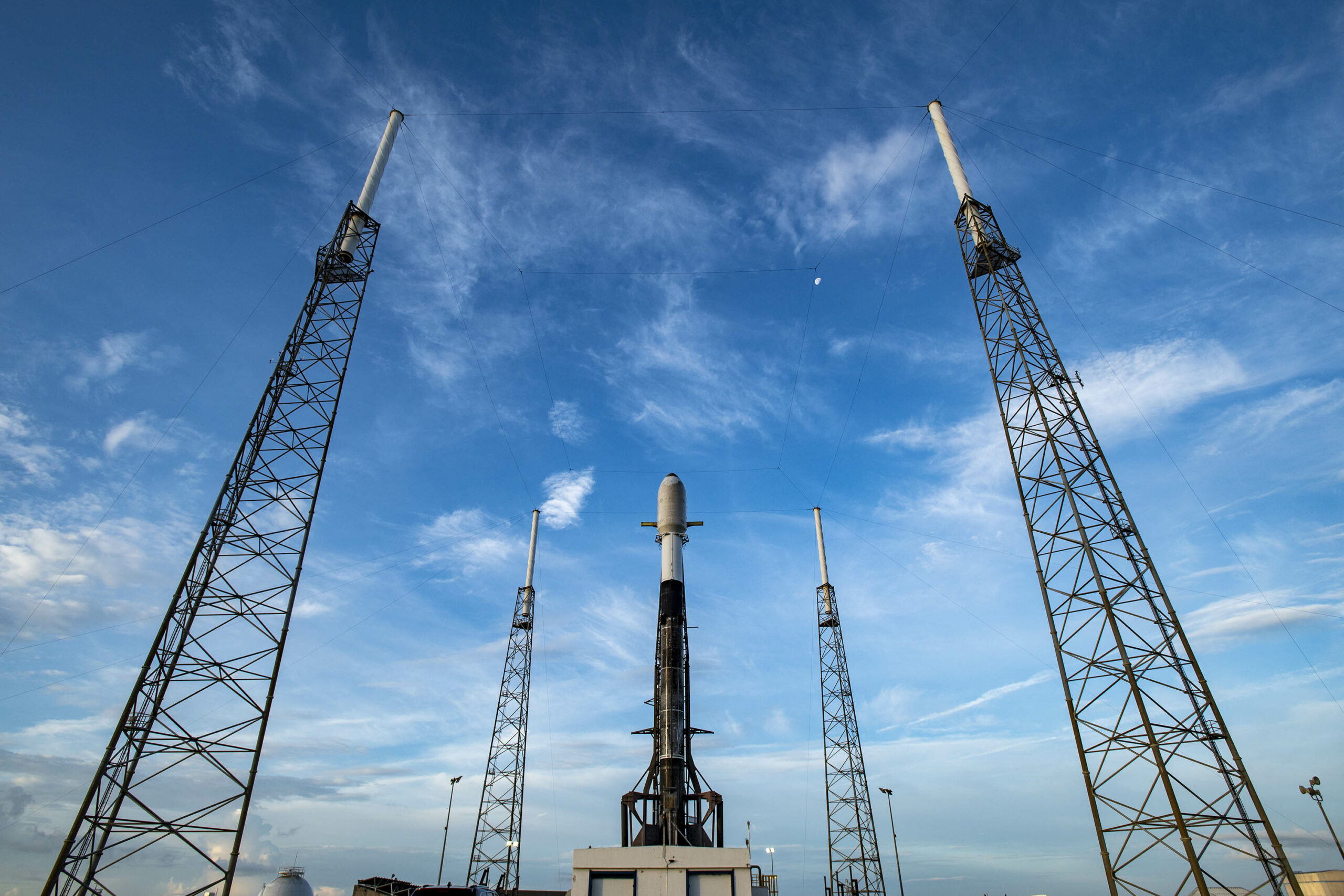
Am Mittwoch, 30. Juni, um 21.31 Uhr MESZ hob eine Falcon 9 von Space X vom legendären Weltraumbahnhof Cape Canaveral, Florida, zu seiner Transporter-2-Mission ab. Mit an Bord: Der ION-Satellitenträger des italienischen NewSpace-Unternehmens D-Orbit auf seiner „Wild Ride“-Mission mit Tech-Passagieren aus 11 Ländern, unter anderem HPS’s ADEO-N2. ION wurde genau eine Stunde nach dem Start vom Launcher erfolgreich ausgesetzt.
Die ION-Plattform wird nun eine Nutzlast nach der anderen auf ihren jeweiligen Umlaufbahnen für In-Orbit-Validierungstests absetzen, bis die Plattform schließlich selbst zum Testobjekt wird, da sie von ADEO, dem weltweit einzigen industriellen NewSpace-Schleppsegel seiner Art für die mehrfache beschleunigte Rückführung ausgedienter Satelliten, wieder „nach Hause“ gebracht wird. Die Idee dahinter: „Haltet den Weltraum einfach „CleanGreen“, indem Ihr nur mit einer Technik an Bord startet, die alles nach Gebrauch auch schnell wieder „nach Hause“ bringt“, sagt Ernst K. Pfeiffer, Geschäftsführer des deutschen Raumfahrtunternehmens HPS. ADEO ist bei HPS in verschiedenen Versionen erhältlich, die auf die Größe und das Gewicht des jeweiligen Raumfahrzeugs zugeschnitten sind. In diesem Fall handelt es sich um eine der kleinsten Versionen mit einem Gewicht von nur 800 Gramm, bei Abmessungen von nur 10x10x10 Zentimetern und einer Segelfläche von 3,6 Quadratmetern.
HPS-Geschäftsführer Ernst K. Pfeiffer ist davon überzeugt, dass ADEO genau zum richtigen Zeitpunkt kam, um eine nachhaltige NewSpace-Entwicklung voranzutreiben, indem die Gefahr von apokalyptischen Weltraummüllszenarien trotz schnell wachsender Konstellationen vermieden wird. Pfeiffer betont in diesem Zusammenhang die exzellente F&E-Unterstützung durch die Ingenieure und Testeinrichtungen des DLR-Instituts für Raumfahrtsysteme in Bremen sowie die verschiedenen Wirtschaftsförderungsverträge und Zuschüsse von ESA, DLR und dem Freistaat Bayern.
Bei der Umsetzung der vom NewSpace-Team der HPS in der Münchner Zentrale entwickelten Technologie legten die Ingenieure und Techniker der rumänischen Tochtergesellschaft und der rumänischen Werkstätten kräftig Hand an. Dies ist nun, so Pfeiffer, „unser klarer Vorteil, alles in einem Unternehmen zu haben: das Erbe aus dem institutionellen Raum, eine maßgeschneiderte „interne Gründungsabteilung“, ein stetig wachsendes Haus in Bukarest und mehrere vertrauensvolle Entwicklungs- und Produktionspartner. Neue und erweiterte Herausforderungen an Innovation und Fertigung warten bereits.“
Am Ende der nominalen ION-Mission, vor den „Augen“ der integrierten Kameras, entfaltet sich das ADEO-Bremssegelmodul, zeigt seine „Flügel“ und führt ION viel schneller als ohne das Segel zur rückstandsfreien Entsorgung durch Verbrennung in der Atmosphäre. Die ersten 100 km des Abstiegs werden intensiv überwacht. Dies soll in einem Missionsslot zwischen Dezember ’21 und Januar ’22 geschehen. Diese Mission ist nun der letzte Nachweis in einer Serie, die auch einen Erstflug mit der Electron von Rocket Lab im Jahr 2019 und mehrere Parabelflüge bis 2021 umfasst.
Mit diesem Live-Beweis technischer Reife geht ADEO dann weiter in Richtung Serienproduktion für bereits wartende Kunden in den USA, Europa und Asien.


Mai 2021
D-Orbit (Italy) and HPS (Germany, Romania) agree on flight for ADEO on ION Satellite Carrier in June 2021
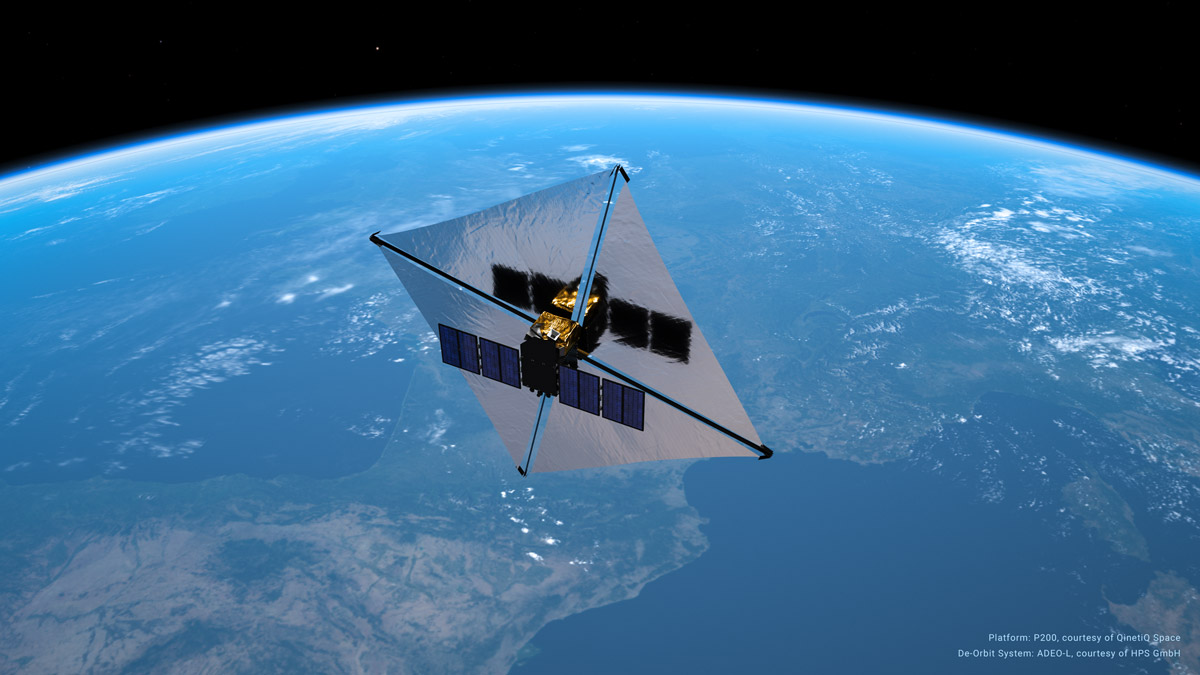
After 6 years of development, including a zero-G parabolic campaign and a first test flight end 2018 with Rocket Lab’s ELECTRON, HPS signed on 30.04.2021 the contract with D-Orbit for the flight of the ADEO-N, named „Show me your Wings“, on the space logistics company’s orbital tranportation vehicle ION Satellite Carrier. The launch of the „Wild Ride“ Mission will take place already summer this year from a launch site in USA.
ADEO, the world’s only industrial NewSpace drag sail of its kind for the multiple accelerated return of retired satellites, is available from HPS in different versions tailored to the size and weight of the spacecraft in question. In this case, it is one of the smallest versions, weighing less than one kilogram, with dimensions of only 10x10x10 centimeters and a sail area of 3.6 square meters. It has been integrated directly into the ION platform at D-Obit now, mid May. ION is a space vehicle that can transport satellites in orbit and release them individually into distinct orbital slots. At the end of the nominal ION-mission, in front of its „eyes“ of the integrated cameras, the ADEO braking sail module unfolds, shows its „wings“ and leads ION to residue-free disposal by incineration in the atmosphere much quicker than without the sail. The first 100 km of descent will be monitored intensively.
HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer is convinced that ADEO came at exactly the right time to promote sustainable NewSpace development by avoiding the threat of apocalyptic space debris scenarios, despite rapidly growing constellations. In this context, Pfeiffer emphasizes the excellent R&D support provided by engineers and test facilities of the DLR Institute of Space Systems in Bremen, as well as the various economic development support contracts and grants provided by ESA, DLR and the Free State of Bavaria.
The implementation of the technology developed by HPS’s NewSpace Team at Munich headquarters was largely supported by the hands of engineers and technicians of the Romanian subsidiary and Romanian workshops. This is now, according to Pfeiffer, our clear advantage having all in one company: heritage from institutional space, a tailored „internal start-up department“, a steadily growing house in Bucharest and several trustful development and production partners. New and expanded challenges to innovation and manufacturing are already waiting.
According to Renato Panesi, co-founder and CCO of D-Orbit: „We are very happy to have a chance to work with HPS on this project: sustainability in general has always been a relevant aspect of our identity, and with HPS we share a common vision aiming to a sustainable access to space. Being able to help HPS to test a new and innovative technology like ADEO to help control the increment of space debris is a point of pride for us. To HPS is reserved the grand finale of the mission and, while we are going to „enjoy the ride“, we are really looking forward to it“.


März 2016
ESA-Prime HPS with SME-Consortium Ready to Build New Generation De-Orbiting Subsystem
Hardly any messages have dominated the space community´s discussions in the past two years as perseverently as these two:
- the debris from past satellite missions forms a growing threat to future endeavors in space
- the number of satellites expected to form future constellations especially on LEO is exploding since new players are discovering space as their domain
- which again multiplies the problem of future debris.
So, on the one hand enormous growth of the satellite business is to be foreseen, on the other hand this business needs better rules in order to be sustainable. „Clean Space“ is ESA´s answer in general and the quest for a new, fully ecological de-orbiting sailsystem in particular.
While currently satellite manufacturers are already facing problems to comply with the 25-years-deorbiting „guideline“ without minimising the effectiveness and increasing the cost of their missions, ESA now aims to make this period as a strict requirement leaving neither ecological nor economical footprints.
Capitalizing on previous research and development in this area like the precursor project ADEO, led by the subsystem prime HPS with its consortium of DLR-institutes in Bremen and Braunschweig and the SMEs Etamax and HTS, ESA now announced its expectations for a full fledged demonstrator ready to fly by 2018 with a deorbiting time of lower than 5 years. The new project will be ignited this year and ESA´s subsystem prime HPS is expected to take this next step towards the final breakthrough in deorbiting technology, too, because:
- the current HPS precursor project ADEO, featuring a 5m x 5m deployable boom and sail subsystem weighing just 20kg, has been successfully tested on breadboard level in February 2016 and will reach design maturity for an Engineering Model manufacturing and assembly through a CDR in these days in March.
- ADEO will then already fulfill the requirements of providing sail and boom materials able to withstand the very severe Atomic Oxygen (AtOx) and Ultra Violet (UV) environment, offering scalability down to 100-kilo-satellites down from the current reference case of spacecrafts at 1-1.5 tons of weight, and of providing reliable deployment technology tested under ambient conditions and in a vaccum chamber in mid 2016.
HPS as ESA subsystem prime is aiming at the follow-on project also with its proven partners.
In parallel and as leading specialist on deployable structures and antennas, HPS Germany acts as prime contractor for Large Deployable Antennas (LDA) in cooperation with the German SME LSS, while the HPS subsidiary in Portugal is working on a deployable highprecision mast system (10-20m) for instruments weighing 100-250 kg on science missions.


Juni 2018
Anlässlich der bevorstehenden Weltraummission „Pride of Bavaria“ zum Test der Nano-Version von ADEO, des künftigen Space-Segel-Subsystems zur schnellen Rückführung ausgedienter Satelliten, besuchte der bayerische Wirtschaftsminister Franz-Josef Pschierer am 24. Mai 2018 die Innovationsschmiede HPS GmbH, München, um sich persönlich von dem Stand des Vorhabens zu informieren.


Neben dieser von Bayern geförderten Entwicklung des weltweit einzigartigen Systems ADEO zur künftigen Vermeidung von Weltraumschrott stellte der Unternehmensgründer und CEO Dr. Ernst K. Pfeiffer bei dem Termin auch die weiteren Produktlinien von HPS vor: Reflektoren für Antennen auf Erdbeobachtungs- und Telekommunikationssatelliten, die derzeit den europäischen Maßstab für hochfrequente Übertragungsqualität setzen, Thermal- und Strahlenschutzsysteme, große im Weltraum entfaltbare Antennen, sowie das hochfeine Netz zur Reflektion der Antennensignale – entwickelt bei HPS, produziert im„Textildreieck“ in der Region der bayerischen Stadt Hof. (Links zum Fernsehsender Sat1 bzgl. Interview: https://www.sat1.de/regional/bayern/videos/die-sendung-vom-25-05-2018-ganze-folge)
Am Samstag, 26. Mai 2018 transportierte die HPS-Crew das Flugmodell sowie das „Flight Spare“ per Flugzeug zum Startplatz.
ADEO wird Ende Juni 2018 von der amerikanischen Rakete ELECTRON der Firma RocketLab von Neuseeland gestartet. (weitere Links: http://spacenews.com/rocket-lab-reschedules-next-electron-launch/; https://www.rocketlabusa.com/)
September 2018
3 million more for next-stage development of deorbit device ADEO
With the support of the German Space Agency delegation HPS has been awarded a 3-million Euro GSTP-contract with ESA for development and manufacturing of a large passive dragsail version of ADEO with presumably about 25 squaremeters in size. The goal of the activity is the delivery of a flight ready protoflight model prepared for an in orbit demonstration mission as early as 2020. Final design and size – on the basis of a market analysis currently undertaken– will be frozen in December 2018.
Like projects on system level, for example, ARIANE, GALILEO and COPERNICUS, ADEO on the subsystem level is classified as one of Europe´s „lighthouse projects“ in space, since
- a solution for fast deorbit of satellites especially from the very crowded LEO orbits at 300-750 km perigee is the absolute prerequisite for sending future single satellites and even whole constellations of short-lived satellites into space in the first place
- ADEO by HPS is Europe´s top chance to gain and keep the globally lead position on the emerging world market with a critical technology ensuring the continent´s independence in space.
- ADEO will in the end address the market commercially and consequently create new jobs as well as contribute to yet another increase of the return-on-investment ratio of public funding in space.

While a 2.5 squaremeter ADEO-N test version is waiting in New Zealand to go on its „Pride of Bavaria“-mission on top of the Electron rocket (#ItsBusinessTime of Rocket Lab USA), this second development – ADEO-L – represents an upscaled version of just 10 Kilo mass and 25 squaremeters enabling passive de-orbiting without the need of any extra propulsion. Due to its virtually unlimited variability and scalability ADEO can be applied to return dead satellites of any size and mass. For example, the current version supported by ESA (and DLR) will reduce the time for disposal of a 500 kg satellite at 650 km altitude from 460 years down to just 11 years, while the small version currently mounted on top of Electron could drag for example a 10 Kilo cube satellite (6U = 30cm x 20cm x 10cm) down from a 500km orbit in 77 days instead of 26 years.
The large version is planned be applied as a protoflight model to a 200-1000kg satellite with an In-Orbit Demonstration as early as 2020. The In-Orbit Demonstration planning phase has already started and HPS is looking among other things for satellite providers that would take the PFM onboard their missions free of charge.
The ADEO subsystem is designed, assembled and tested by HPS as prime contractor of ESA and supported by eight subcontractors, 5 of them being SMEs. Main subcontractors are DLR institutes Bremen and Braunschweig and RUAG Space Germany (formerly HTS).
