January 2025
ADEO – Space Heritage
ADEO (Atmospheric Deorbit Sail Module) is the name for an entire product family of drag sails for satellites from the German space company HPS, Munich. They accelerate the disposal of satellites from space to a period of less than five years and thus fulfill the prerequisite for the satellite to receive approval for launch into space in the first place.
The sail is scalable and available in many variants from series production. ADEO-N is tailored to small satellite missions of 20-250 kg, while the ADEO-M and ADEO-L series are designed for larger missions of 100-700 kg and 500-1500 kg respectively. The ADEO-N series corresponds to a sail size of 5±2 m2, while ADEO-M covers areas of 15 ± 5 m2 and ADEO-L 25 m2 and more. However, smaller versions have also been available for a year, especially for cubesats, e.g. an ADEO-P for 1U-6U satellites (1-20 kg) and an ADEO-C for larger cubesats (5-50 kg). A total of five versions are currently available to order, all of which reliably dispose of satellites from LEO – including those from higher MEO orbits when combined with satellite’s onboard propulsion – within the required time frame. A corresponding configurator for selecting the perfectly suitable ADEO module is available for individual mission calculation (ADEO Online Configurator).
Now there is a short film about the production and testing of the product family, as well as ADEO’s heritage story:
Based on over ten years of development, HPS has successfully completed a series of missions up to “full burn” and has thus firmly established itself at the top of deorbit technologies at qualification level TRL 9.
2018: ADEO-N1 (“NABEO”) was launched on a Rocket Lab Electron rocket kick stage back in 2018, with Peter Beck himself (CEO RocketLab) even personally handling the sail. On this flight, the sail was unfurled just 90 minutes after the launch. Visual ground observations confirmed the successfully deployed sail and its performance.
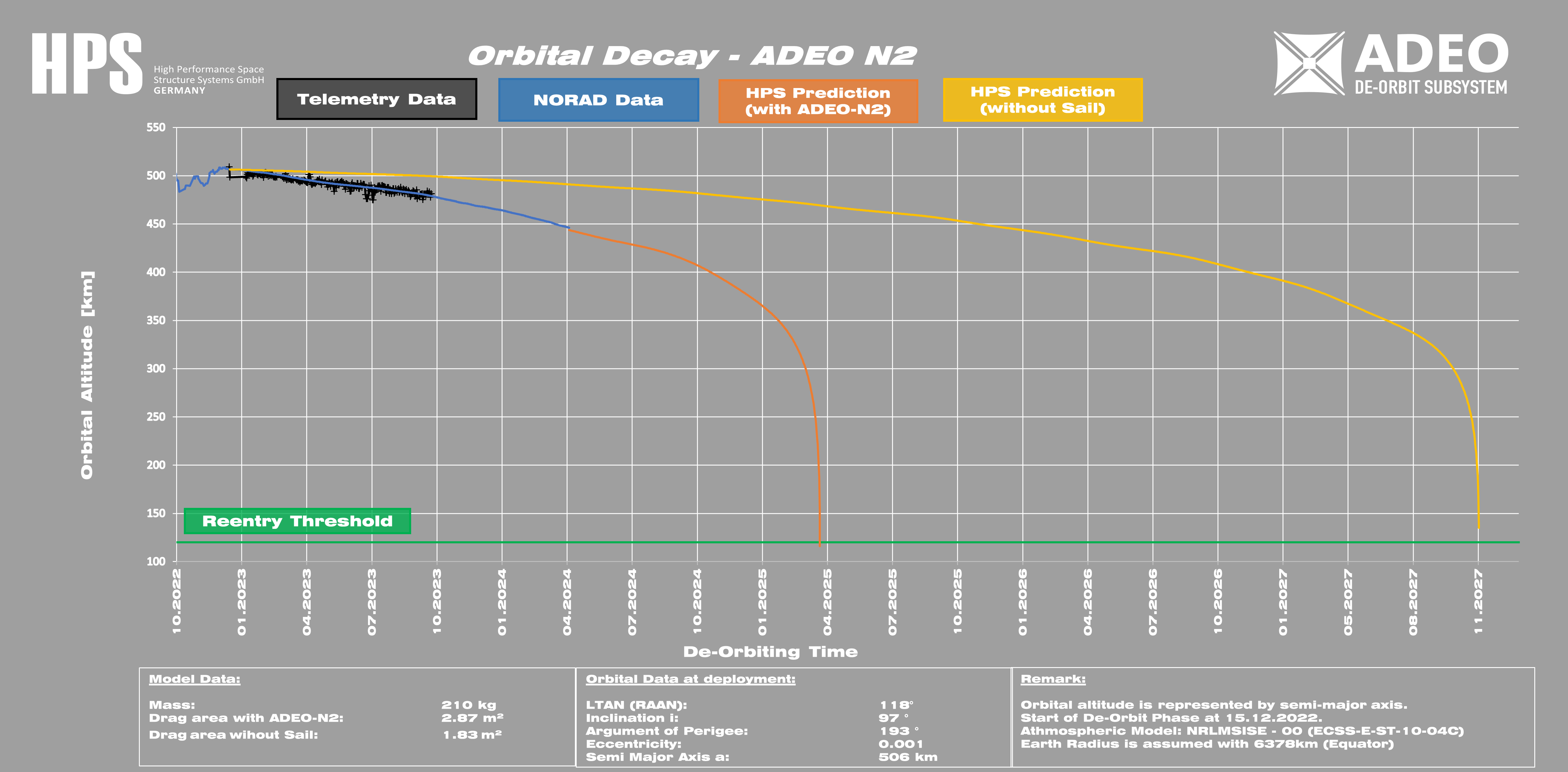
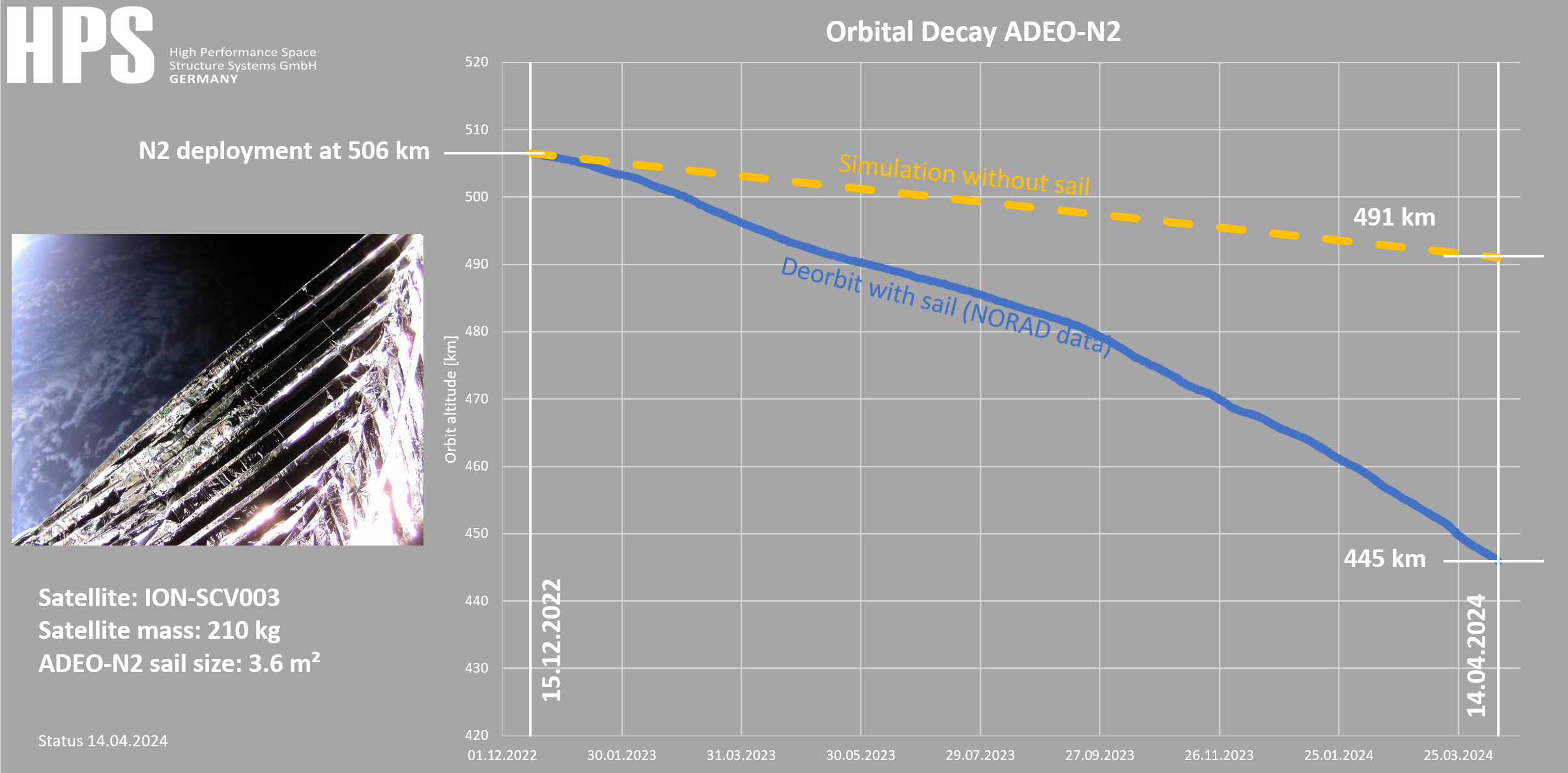
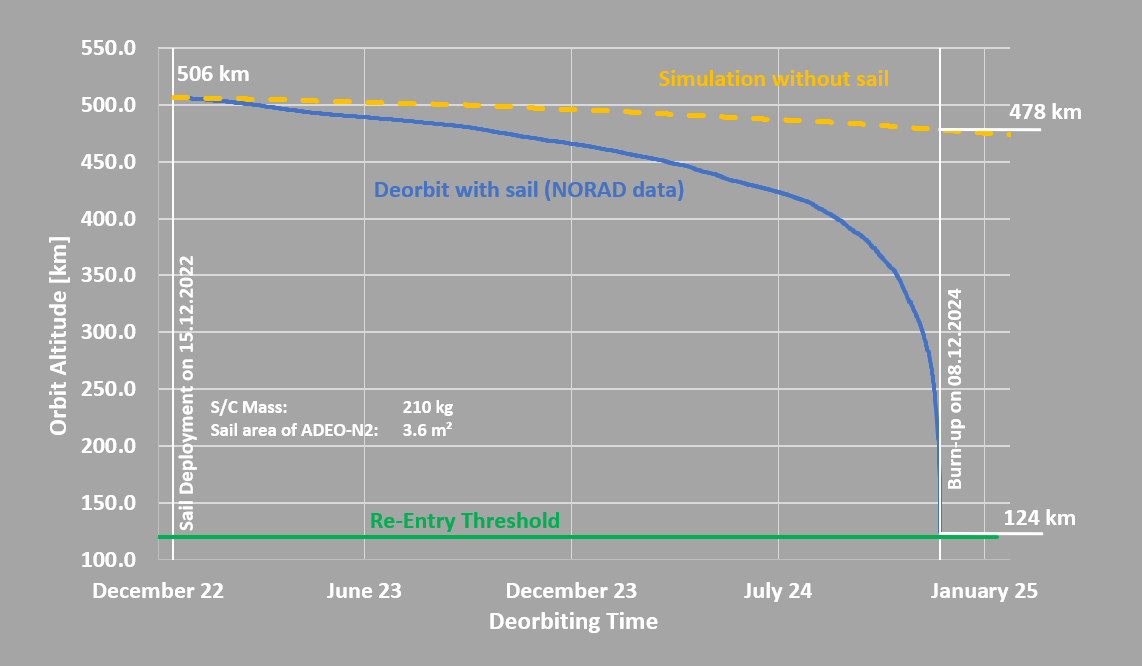
2021: In June 2021, ADEO-N2 (“Show me your Wings”) was launched into space by the spacecraft carrier ION-003 of the Italian launch service provider D-Orbit, as part of SpaceX’s Transporter-2 mission. The successful deployment of the sail in December 2022 was recorded by the ION carrier’s on-board camera. The integrity of the sail after one year in orbit was confirmed, again by means of the onboard camera. On December 8, 2024, HPS received confirmation that ADEO-N2 had completed its mission with deployment of the dragsail at 506 km orbit altitude in a record time of just two years after the 210 kg satellite’s “end-of-business” with fireworks of success at 120 km orbit altitude, beating international rules and regulations by three full years.
Even NASA ranks the ADEO module from HPS as the number one automatic passive deorbit technology in view of the qualification and Flight Heritage.
ADEO is now a bestseller not only with European institutions and companies, but also in the fully commercial markets of the USA and Canada.
Highest qualification levels, proven reliability and flight heritage combined with scalability, availability and attractive pricing make the ADEO product family a highly visible beacon in the global field of deorbit systems for all satellites that must comply with the new 5-year deorbit requirement to obtain launch authorization.
Click here for the latest clip about ADEO
————————-
Video: © HPS GmbH, Munich, Germany, www.hps-gmbh.com
Production: Daniela Creutz, www.bluecirceproductions.com
————————-
WILD RIDE mission ends with fireworks of success for deorbit sail ADEO-N2
Three days ago, on December 8, 2024, HPS received confirmation that ADEO-N2 completed its mission with launch in 2021 and end-of-business with deployment of the dragsail at 506 km orbit altitude in December 2022 in a record time of only two years with a firework of success, beating international rules and regulations by three full years. This is further proof of the success of the German ADEO model, which is manufactured in series production by the German world market leader HPS for all sizes of LEO satellites in five ADEO versions. ADEO fulfils the “5-year rule” already issued by several states and organizations for obtaining launch and operating permits for satellites, and with “Wild Ride” this has now even been verified in orbit by precisely tracking the deorbit curve until the satellite burns up completely at an orbital altitude of approx. 127 km (see image).
About the mission:
On June 30, 2021, D-Orbit, a leading company in the space logistics and orbital transportation industry from Italy, announced the successful launch of another ION Satellite Carrier (ION SCV 003), its proprietary orbital transport vehicle. It lifted off at 9:31 p.m. CEST on June 30, 2021 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS), Florida. That same day, 60 minutes after launch, the vehicle was successfully placed into a 500 km high Sun Synchronous Orbit (SSO).
ION Satellite Carrier is a space transporter developed, manufactured and operated by D-Orbit. ION is capable of accommodating multiple satellites, transporting them into space, performing orbital maneuvers and precisely releasing them into dedicated orbital positions.
At the end of the so-called WILD RIDE mission, the ION SCV 003, weighing 210 kg at the time, entered the deorbit phase on December 15,2022 with the deployment of ADEO-N2 (effective sail size 3.6 m2, christened “Show me your Wings”) entered the deorbit phase and began testing the world’s first precise functional in-situ verification of a dragsail, with official “end of flight” on 08.12.2024 [source: NORAD], i.e. within exactly 2 years in a completely natural way and without exhaust gases from any propulsion system. Without sails, SCV-003’s deorbit would have taken twice to three times as long.
About ADEO:
ADEO-N is a 1U-sized deorbit sail module developed by the German space company HPS, in cooperation with several companies and institutions (e.g. DLR and Fraunhofer), co-funded by the ESA-GSTP program, the German national technology program, and the Bavarian technology program. In accordance with the new rules, ADEO ensures the removal of end-of-life satellites from LEO within a maximum of 5 years.
November 2024
HPS and EXOLAUNCH: Making Space Clean Again
HPS is happy to join forces with the Germany-based Exolaunch and is fully engaged to support customers of Exolaunch by enabling this very special and successful NewSpace-launch service provider to grant priority access to the delivery schedule of flight-proven ADEO* deorbit sails which are currently in high demand.
EXOLAUNCH’s COO Jeanne Allarie and HPS’s CEO Ernst Pfeiffer signed an Agreement on Space Tech Expo 2024 in Bremen in a great joint spirit (see pictures) the ambitious endeavour of
- being a role model for a sustainable use of space and
- of raising awareness with all potential customers on an existing solution for deorbiting: ADEO-modules are easy, affordable and reliable to contributing significantly to Making Space Clean Again.
See for the respective EXOLAUNCH announcement
(* ADEO-modules are needed to allow a satellite deorbit after its “End-of-Business” within five years; satellites without this or any kind of deorbit accelerator do not get clearance for launch anymore.)



October 2024
Clean Space Days der ESA im Oktober: ADEO aus dem Hause HPS im Fokus
In 2024, the ESA’s Clean Space Team once again invited participants to the continuation of the past Clean Space Days.
The four-day event will focus on progress in the areas of eco-design, zero debris and in-orbit maintenance.
The calendar of presentations in 2024 will highlight these topics, among others:
- Life cycle assessment for space activities
- Deorbit technologies
- Debris disposal
- Disturbance-free skies for astronomy
- IOS missions
- Circular economy for space travel
While some presentations tended to highlight ideas and technical concepts in statu nascendi, HPS manager Frank Hoffmann presented the ADEO product family, which is already successful on the European and, more recently, North American markets: Deorbit sail technology for automatic self-disposal of the satellite at the end of the mission.
The ADEO system offers a suitably customized solution for every class of spacecraft, whether as a “Pico” (1-20 kg), “Cube” (5-50 kg), “Nano” (20-250 kg), “Medium” (100-700 kg) or even “Large” (500-1500 kg). To ensure that satellite manufacturers are supplied without delay, all orders are handled by HPS directly from series production wherever possible.
Due to the fact that the requirement to carry a suitable disposal system such as ADEO is a prerequisite for launch authorization for practically all satellites from October 2024, longer delivery times are possible and can be largely avoided by ordering early.
The Clean Space Days will come to an end at the end of the week, but the saying “after the event is before the event” also applies to this successful European space event.

September 2024
ADEO Pico: The smallest dragsail gains a foothold in the largest market
Deorbit Technology from HPS
With the ink now drying under the contract for a PICO-class satellite deorbit device from the ADEO dragsail family of HPS, the Munich-based space technology company is now also setting foot on North American soil: After careful consideration of the alternatives, the Canadian company StarSpec Technologies decided in favor of the system for integration on their InspireSAT 12U ADCS MVP satellite, to be launched in 2026.
The ADEO-P was purchased at the beginning of July. The integration will be carried out by the experts in 2025. The satellite is planned to be launched in 2026 aboard a Falcon9 as part of the Transporter-17 SmallSat Rideshire mission from the Vandenburg Space Force Base in the USA. At the end of the mission, the dragsail will be deployed to a size of 1.4 m2 and automatically dispose of the satellite within the now obligatory period of less than five years. The satellite will burn up in the atmosphere without leaving any residue.
This initiative promotes StarSpec’s high precision space-qualified ADCS components, including sub-arcsecond precision star cameras, cogless reaction wheels, and ultra-high-bandwidth controllers, providing 100x the precision and imaging quality for LEO imaging satellite.
Jason Brown, Mechanical & Technology Lead, commented on the key factors leading to the selection of the ADEO-P for InspireSAT: “A primary mandate of InspireSAT is to provide high performance in-orbit capabilities in a way that does not compromise and strongly maintains the continued and future utility of LEO. We are delighted to have HPS, a proven high-tech specialist in the international space industry, at our side, allowing StarSpec Technologies to maintain its sustainable and orbit-conscious approach to space in a way that maintains focus on the successful demonstration of our transformative state-of-the-art ADCS. Thanks HPS!”

August 2024
ESA: 1 million for product innovation by HPS, AAC and DLR
ESA’s GSTP program is one of the European Space Agency’s most important instruments for promoting new technologies, particularly those generated by SMEs. The program also enjoys high priority in the overall ESA portfolio at the German space agency; the corresponding financial resources now also enable the launch of a new sub-program called “Product Initiative”. With the signing of the contract on August 7, 2024, ESA and HPS as the main contractor gave the go-ahead for the first technology project in this category.
It took just over six months from the idea to the signing of the contract; the funding amount is one million euros. The Munich-based space technology company HPS and its long-standing partner, Vienna-based Aerospace & Advanced Composites GmbH, are contributing 20 percent of their own funds, while the DLR Institute of Space Systems in Bremen is also on board on the research side. Over the next 24 months, highly innovative films (working name “ProFilm”) will be developed in various thicknesses and surface configurations and for large-area applications, which are characterized by two special features in particular:
- they are resistant to the chemically aggressive residual oxygen molecules (ATOX-resistant) and are therefore perfectly suited for use in particular in the highly frequented low earth orbit LEO area,
- Special derivatives are invisible or non-reflective.
In addition to use as thermal insulation for satellites, this also results in innovative applications as invisible brake sails as a further development of the HPS ADEO product range for deorbiting decommissioned satellites.
In this way, they serve four strategic goals of European space:
- Securing technological independence from other major spacefaring nations that have already made progress in this area
- Support European manufacturers of spacecraft and satellites, for whom maximum physical protection is an element of the competitiveness of their products
- Avoidance of astronomy-hostile light pollution in space through non-reflective surfaces on dragsails and thermal insulation such as MLIs and SLIs. There are also plans to use them for solar panels and radiators.
The ideas go as far as deployable structures that could make entire satellites invisible with ProFilm.
HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer is enthusiastic about the start of the project: “The innovation processes that have now been initiated will result in highly exciting products – the cooperation with our partners, DLR in the north and AAC GmbH in the south, alone is a guarantee of this. Above all, however, this premiere of ESA’s new GSTP sub-programme shows how quickly and effectively the European space agency can identify, accept and master technical challenges. This is exactly what European space travel needs, and this is exactly what innovation drivers from the ranks of SMEs need in particular.”

ESA pushing market-driven series production with co-financing of 1.2 million euros
July 2024
ADEO deorbit sail system from HPS
Space-related technologies should be clean and sustainable, because only then access to space will remain possible for future generations. This topic, which is currently a top priority of space policy, has led to a number of technical solutions which are now available on the market, with the ADEO deorbit system from HPS leading the way. Being recognized even by NASA, the ADEO dragsails ensure already before launch that satellites will not turn into space debris at the „end-of-business“. Instead, they re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere.
The European Space Agency ESA, as well as its national counterpart DLR and the Bavarian Ministry of Economic Affairs, has consistently supported the twelve years of development of this product by HPS. The sharp increase in demand from customers, particularly in the CubeSat and SmallSat sector from Europe, but also from North America and even Asia, is driven by the simple fact that both ESA, for European launches, and the FCC, for American launches, now demand on-board systems to be able to deorbit a satellite in just 5 years instead of the previous 25 years. Also SpaceX confirms that no more satellites will be launched without complying to this requirement.
With the ADEO variants “Pico”, “Cube”, “Nano”, “Medium” and “Large”, HPS meets the market demand for all sizes of LEO satellites in orbits between 300 and 900 kilometers. All variants are already in production, with manufacturing at the HPS production sites in Munich (Germany) and Bucharest (Romania) which are closely working together. Nevertheless, HPS and the technical ADEO experts at ESA have identified a number of optimization and expansion opportunities in order to urgently increase the pace of the series production and in response to the increasing price pressure of the New Space scene. The company is now raising the required funds for the implementation of these opportunities in the short term, using co-financing of 1.2 million euros signed by ESA on June 28, 2024.
ESA-Director Dietmar Pilz for Technology, Engineering and Quality in a videocon on July 1st: „my best wishes for this important technology development.“
HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer: “As a company, we are very pleased about the trust and continuous support from the European Space Agency, and therefore indirectly also from the German Ministry of Economic Affairs. However, this is at least as much a reason for joy for all those who, thanks to its technology programs such as GSTP, would like to see Europe in a leading role in the development of components for space technology and -transport, especially in the commercially so important LEO and MEO supplier market.


ESA’s priorities here are not only clear, but are also being consistently implemented. One milestone was the recent signing of the Zero Debris Charter in Berlin. The upcoming optimization of series production and the enhancement of our ADEO product portfolio, while maintaining the same level of quality and reliability, will effectively help to face the upcoming peaks in global orders, including those received very late, and thus still enable the launch of these satellites. We shareholders see our own funds, in the 7-digit range over the years, on the one hand as an investment in a strong future for HPS, and on the other hand as our moral obligation to make a contribution to the sustainable use of space.”
HPS Signing of the Zero Debris Charter at ILA on June 6, 2024
June 2024
ESA Leads the Way: Rapid Implementation of the Zero Debris Charter
Sustainability in space travel has also been an issue for the European Space Agency ESA for years. However, only a few months passed between the decision to adopt a Zero Debris Charter and its implementation.
Keynote speaker ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher also saw this as a sign that the time is finally ripe for concrete steps instead of pure symbolism, especially as ESA itself has provided significant impetus for the development of the two main technologies on the way to “Zero Debris”: firstly, ways of removing scrap from space, but above all, equipping satellites with deorbit technology from the outset so that no more waste is produced after the end of the mission.

ADEO Drag Sail: The Key to Sustainable Spaceflight
The ADEO brake sail, which is now available as an entire product family for all sizes of LEO satellites from HPS series production, stands for this. In addition to grants and support from ESA, DLR and Bavaria, HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer also invested a lot of the company’s own money in the project, always firmly convinced that the hour of ADEO would come sooner or later – and if a little later, then all the more powerfully.
It was exactly the same when, in mid-2023, the ESA set the new rule of a deorbit maximum of 5 years for ESA-funded missions instead of the previous 25 years, and, accordingly, LEO satellites without ADEO (or similar) will no longer be launched at all from October 2024, as SpaceX, for example, makes clear in its conditions of carriage in accordance with FCC regulations.

Historic Moment: 12 Nations Sign the Zero Debris Charter
The Charter was signed in Brussels on May 22 by 12 countries, including Germany. Since then, over 100 organizations, companies and entrepreneurs have been waiting for their cue to sign.
The ILA 2024 marks a very important stage on this path towards the sustainability of European space travel and sets an example for companies on other continents.

May 2024
Update on ADEO´s Performance
After 487 days of approachflight towards Earth, ADEO-N2 on the ION SCV 3 test satellite continues to sail on a record course without even a scratch: the current position has been reached in a threefold shorter time of the ADEO deorbit compared to the classic missions, whose data are subject to the prediction algorithms.
Expected touchdown at the edge of the Earth’s atmosphere: April 2025.
This is reported by the two mission managers, D-Orbit, Rome (satellite) and HPS, Munich (brake sail).
February 2024
HPS with ADEO in top position in NASA’s technology report
Since its inception, the U.S. space agency NASA has been the primary driver of progress in aerospace technology. NASA’s Scientific and Technical Information (STI) program plays a key role in ensuring that NASA maintains this important role. Its Technical Reports Server contains one of the largest collections of aerospace science STI in the world, including “Technical Publications” on critical research and achievements of lasting value.
Focus on deorbit technologies
The aim of the latest publication, published in February 2024, on groundbreaking technologies, particularly in the field of small satellites, is, among other things, to present the world’s leading deorbit technologies, which can be used to technically implement the new regulation on the disposal of LEO satellites, which has been sharply limited from 25 to 5 years in both the USA and Europe. In its evaluation criteria for technologies, NASA is primarily guided by the TRL standard of the respective products and also pays great attention to the scalability achieved.
ADEO has it all: top values up to TRL-9, scalability and flight successes
According to NASA, the deployable brake sail system ADEO from HPS occupies the leading position on the global market in the category of passive deorbit systems. This is because ADEO not only offers technological maturity up to the peak value of TRL-9, but also a successful flight heritage and is also prepared for equipping various small satellite formats thanks to the HPS series production of an entire product family. This broad protection of HPS’s leading position with ADEO has been widely recognized by NASA – despite the fact that it is a competitor with several projects in this field:
“The Drag Augmentation Deorbiting System (ADEO) is a drag sail developed by the German company High Performance Space Structure Systems (HPS). The sail is scalable and HPS has already launched a number of missions with different configurations up to TRL 9. The ADEO-N series is tailored for small satellite missions of 20-250 kg, while the ADEO-M and ADEO-L series are designed for larger missions of 100-700 kg and 500-1500 kg respectively. The ADEO-N series corresponds to a sail size of 5±2 m2, while ADEO-M covers areas of 15 ± 5 m2. There are also smaller versions, especially for picosatellites (ADEO-P) and CubeSats (ADEO-C), and the possibility to configure the sail size according to customer requirements. Various missions have already tested the ADEO-N product family. The NABEO-1 was launched on a Rocket Lab Electron rocket kick stage in 2018. The sail was deployed just 90 minutes after launch. There was a problem measuring whether the drag sail was initially deployed, but visual ground observations confirmed successful deployment and performance. At the end of December 2022, the ADEO-N2 sail was launched into space by the ION-2 spacecraft carrier of the Italian launch service provider D-Orbit. The successful deployment was recorded by the ION carrier’s on-board camera.”
ADEO – Deorbit technology as a prerequisite for launch authorization
With this presentation in one of the most important technology documentations of the US space agency NASA, HPS with ADEO becomes a highly visible beacon in the worldwide field of passive deorbit systems for all satellites that have to comply with the new 5-year deorbit requirement in order to be approved for launch by American or European launchers